入れ子の、親子同士や上下間のmarginの相殺
公開:2015-08-14
更新:
CSSのmarginで、入れ子(ネスト)にした子要素のmarginが親からはみ出る場合に、親子同士や上下間で相殺される様子を色々試し、そのソースコードと結果の図です。
別の記事で
ことを確認しました。このページはその両方を足したものです。予想はつくでしょうが、やはり物は試しなので実験してみます。
基本形

先ず入れ子にした要素を上下に配置します。親要素のborder・padding・heightはありません。
- 親要素=parent=薄い色
- 子要素=child=濃い色
現時点では各要素のmarginは0(ゼロ)としています。
<div class="boxA-parent"> <div class="boxA-child""> <p>boxAp/Ac</p> </div> </div> <div class="boxB-parent"> <div class="boxB-child"> <p>boxBp/Bc</p> </div> </div>
.boxA-parent {
background-color: pink;
width: 150px;
margin-bottom: 0;
}
.boxA-child {
background-color: red;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-bottom: 0;
}
.boxB-parent {
background-color: lightblue;
width: 150px;
margin-top: 0;
}
.boxB-child {
background-color: blue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-top: 0;
}
(見やすくするために上記以外に背景にグリッド状の画像を並べるなど多少の装飾をしています。)
入れ子の、親子同士でのmarginの相殺
上の親子だけに、親子それぞれにmarginを指定します。
上の親要素のmargin大
.boxA-parent {
background-color: pink;
width: 150px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
}
.boxA-child {
background-color: red;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}

上の子要素のmargin大
.boxA-parent {
background-color: pink;
width: 150px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.boxA-child {
background-color: red;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
}

100 + 50 = 150px とはならずに親子どちらかの大きい方のみが適用されました。
今回は記載しませんが、上向きのmarginでも同様です。
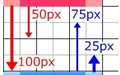
入れ子の、上下間のmarginの相殺
上下の親子全て、上下間のmarginを指定します。
.boxA-parent {
background-color: pink;
width: 150px;
margin-bottom: 100px;
}
.boxA-child {
background-color: red;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.boxB-parent {
background-color: lightblue;
width: 150px;
margin-top: 25px;
}
.boxB-child {
background-color: blue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-top: 75px;
}

同様に各marginの値を変えてみるとこうなりました。


実際の様子
「入れ子の、親子同士や上下間のmarginの相殺」のまとめ
入れ子ではない場合と同様に
- 上下の要素間のmarginが相殺される
- 入れ子の子要素のmarginが親要素からはみ出る
となりました。いずれも全ての中で最も大きい値のみが適用されました。
ただし、冒頭に書いた通りこれは親要素のborder・padding・heightいずれもない場合で、これらがあると違いが出てきます。それは以下の関連記事でご確認願います。
ちなみにpaddingの場合は相殺されません。
 Web制作実験
Web制作実験